Table of contents
I'm starting my journey on Web3, and I'd love to share the experience with you. Here's all you need to know about Web3.
What is Web3?
Web3 is the next third generation of the internet, in which websites and applications will be capable of processing information in a human-like manner using big data, machine learning (ML), and decentralized ledger technology (DLT), among other technologies. Tim Berners-Lee, the creator of the World Wide Web, initially referred to Web3 as the Semantic Web, with the goal of creating a more intelligent, autonomous, and open internet.
The Evolution of the Internet
So far, the Internet has gone through a period every 10 years, progressing from Web1 to Web2 to Web3. Surprisingly, there is no one governing body driving these stages, nor is there a consistent line for when the Internet transitions from being controlled by Web1 to being dominated by Web2. Nonetheless, the nature of Internet material distinguishes these several times. Simply put, the three phases of the internet are as follows:
- Web1 – Static
- Web2 – Dynamic
- Web3 – Decentralized
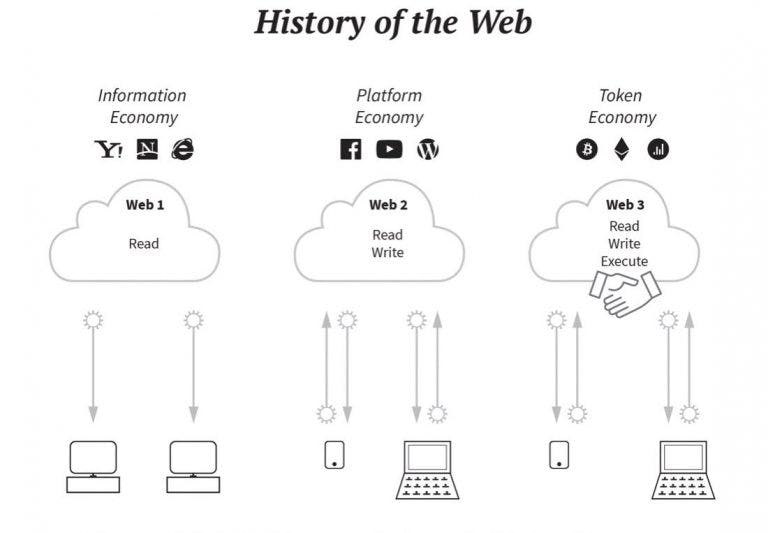
Web1
Web1, the first version of the internet, operated from the early 1990s through the mid-2000s, and was distinguished by static or read-only website pages. This form of the internet was created by web developers to provide largely text and visuals to users, who could just consume the material but not engage with it.
Web2
Web2, the current version, is an invention of the Dotcom Bubble burst (investopedia.com/terms/d/dotcom-bubble.asp), in which the first rush of investment in internet-based enterprises resulted in losses. This was momentous because it helped to weed out frauds and showcase true success stories, laying the groundwork for subsequent successful internet enterprises. While Web2 may be defined as the point at which the internet became an interactive and social web, allowing anybody with access to generate content, it is far more than that.
Web 2.0 is defined by tech businesses that create their own platform atop the open layer of the internet and lock it in while delivering a great user experience that discourages people from leaving. Apps in this generation of the internet are designed in such a manner that users may become innovators. Web 2.0 applications include Google, YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and other social media platforms.
Web2 firms create slick and groundbreaking applications that rapidly gain recognition, and as the app's popularity grows, so does its client base. While these programs are free to use, end-users pay by accidentally providing their personal information, which Web2 businesses sell to advertising and, occasionally, political campaigns. As a result, in less than two decades, several of these firms have risen to be the most significant in history.
Web3
Web3 is a new version of the internet that uses blockchain to "decentralize" administration, eliminating corporate control to make it more democratic. It is identified by open-source software; it is trustless—that is, it does not need the assistance of a trusted third party—and it is permissionless (has no governing body).
Web3 advances the internet as we know it today by adding a few new features. Web3 stands for:
- Trustless
- Verifiable
- Permissionless
- Self-governing
- Distributed and robust
- Native built-in payments
Developers in Web3 do not often design and deploy apps that operate on a server or store their information in a single database, which is typically hosted and maintained by a cloud provider. Instead, Web3 apps, operate on blockchains, decentralized networks of numerous peer-to-peer nodes, or a mix of the two that constitutes a cryptoeconomic protocol. These applications are referred to as "decentralized apps."
Whenever you hear about Web3, you'll notice that bitcoin is often mentioned. This is due to the fact that bitcoin plays a significant part in many of these systems. It offers a financial incentive (tokens) to anybody who wishes to help create, control, contribute to, or improve one of the projects itself. These protocols often provide a range of services such as computation, storage, bandwidth, identification, hosting, and other online services formerly supplied by cloud providers.
Although the notion of Web3 isn't completely established, platforms that represent the concept already exist, and they offer opportunities for individuals to collaborate and earn money. Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAO), DeFi platforms, crypto gaming platforms, and even the metaverse are examples of such platforms.
Conclusion
The new web will provide a more personalized and tailored surfing experience, a faster and more human-like search engine, and other decentralized advantages that are intended to contribute to the establishment of a more balanced web. This will be accomplished by enabling each user to become a supreme over their data and generating a richer overall experience as a result of the plethora of innovations that will be implemented once it is in place.
